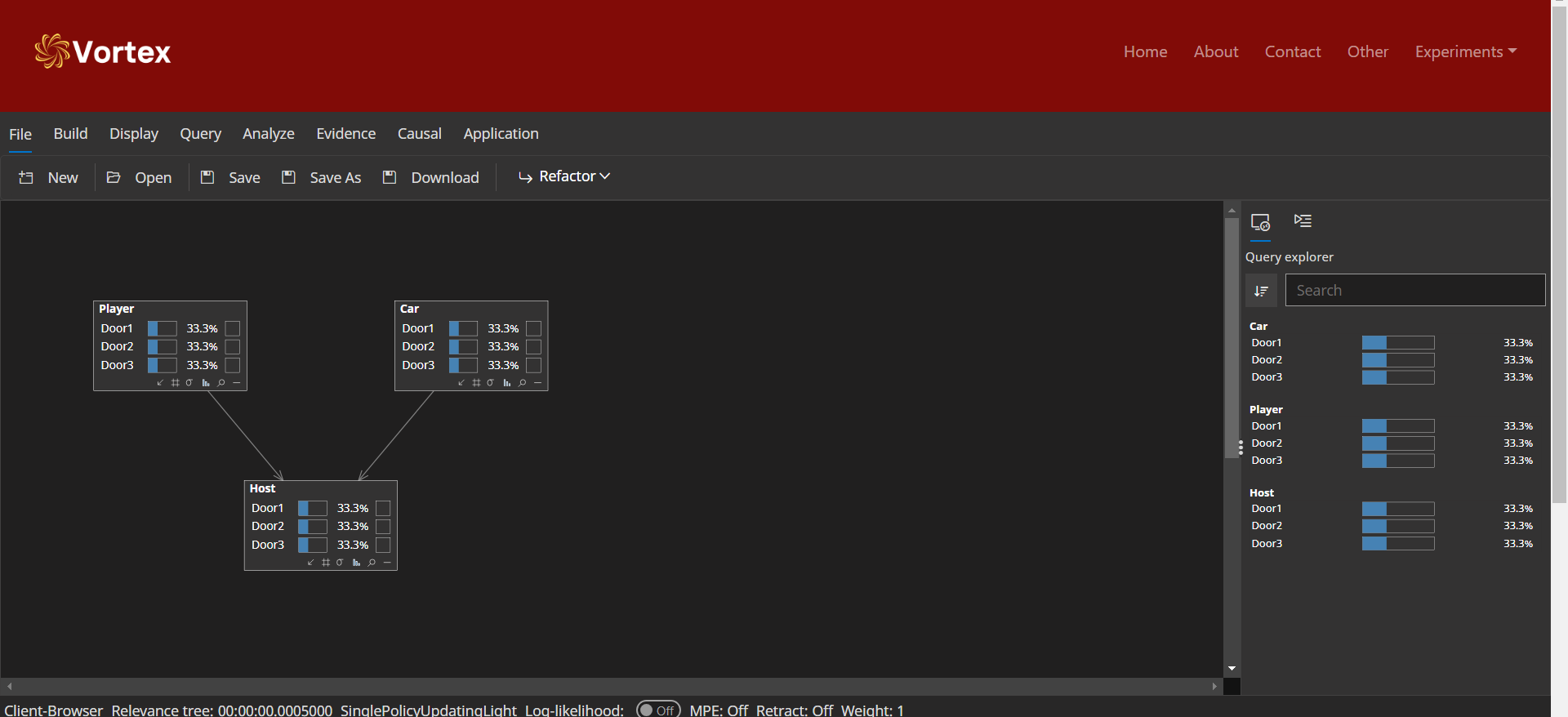
| 1. Introduction to Probabilistic Graphical Modelling |
Introduction to Probability Theory: |
Probability Theory |
|
|
Basic Concepts in Probability |
|
|
Random Variables and Joint Distribution |
|
|
Independence and Conditional Independence |
|
|
Continuous Spaces |
|
|
Expectation and Variances Theory of Predicate Calculus |
|
|
Mathematical Induction |
|
Introduction to Graphs: |
Nodes and Edges |
|
|
Subgraphs |
|
|
Paths and Trails |
|
|
Cycles and Loop |
|
Introduction to Probabilistic Graph Models: |
Bayesian Network |
|
|
Markov Model |
|
|
Hidden Markov Model |
| 2. Bayesian Network Model and Inference |
Directed Graph Models: |
Bayesian Network Exploiting Independence Properties |
|
|
Naive Bayes Model |
|
|
Bayesian Network Model |
|
|
Reasoning Patterns |
|
|
Basic Independencies in Bayesian Networks |
|
|
Bayesian Network Semantics |
|
|
Graphs and Distributions |
|
Modelling: |
Picking variables |
|
|
Picking Structure |
|
|
Picking Probabilities |
|
|
D-separation |
|
Local Probabilistic Models: |
Tabular CPDs |
|
|
Deterministic CPDs |
|
|
Context Specific CPDs |
|
|
Generalized Linear Models |
|
Exact inference variable elimination: |
Analysis of Complexity |
|
|
Variable Elimination |
|
|
Conditioning |
|
|
Inference with Structured CPDs |
| 3. Markov Network Model and Inference |
Undirected Graph Models: |
Markov Model-Markov Network |
|
|
Parameterization of Markov Network |
|
|
Gibb's distribution |
|
|
Reduced Markov Network |
|
|
Markov Network Independences |
|
|
From Distributions to Graphs |
|
|
Fine Grained Parameterization |
|
|
Over Parameterization |
|
Exact inference variable elimination: |
Graph Theoretic Analysis for Variable Elimination |
|
|
Conditioning |
| 4. Hidden Markov Model and Inference |
Template Based Graph Model : |
HMM- Temporal Models |
|
|
Template Variables and Template Factors |
|
|
Directed Probabilistic Models |
|
|
Undirected Representation |
|
|
Structural Uncertainty |
| 5. Learning and Taking Actions and Decisions |
Learning Graphical Models: |
Goals of Learning |
|
|
Density Estimation |
|
|
Specific Prediction Tasks |
|
|
Knowledge Discovery |
|
Learning as Optimization: |
Empirical Risk |
|
|
Over fitting |
|
|
Generalization |
|
|
Evaluating Generalization Performance |
|
|
Selecting a Learning Procedure |
|
|
Goodness of fit |
|
|
Learning Tasks |
|
Parameter Estimation: |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation |
|
|
MLE for Bayesian Networks |
|
Causality: |
Conditioning and Intervention |
|
|
Correlation and Causation |
|
|
Causal Models |
|
|
Structural Causal Identifiability |
|
|
Mechanisms and Response Variables |
|
|
Learning Causal Models |
|
Utilities and Decisions: |
Maximizing Expected Utility |
|
|
Utility Curves |
|
|
Utility Elicitation |
|
Structured Decision Problems: |
Decision Tree |
| 6. Applications |
Application of Bayesian Networks: |
Classification |
|
|
Forecasting |
|
|
Decision Making |
|
Application of Markov Models: |
Cost Effectiveness Analysis |
|
|
Relational Markov Model and its Applications |
|
|
Application in Portfolio Optimization |
|
Application of HMM: |
Speech Recognition |
|
|
Part of Speech Tagging |
|
|
Bioinformatics |