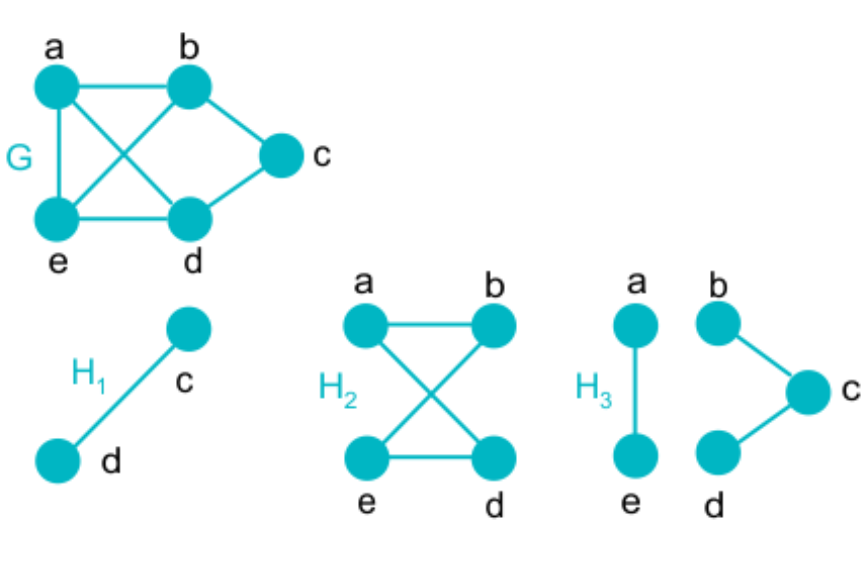
Nodes and Edges
A graph is a structure that comprises a set of vertices and a set of edges. Directed graphical models can be represented by a graph with its vertices serving as random variables and directed edges serving as dependency relationships between them.
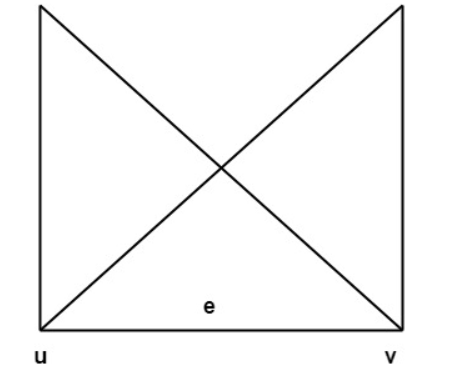
- A set V=V(G) whose elements are called vertices, points or nodes of G.
- A set E = E(G) of an unordered pair of distinct vertices called edges of G.
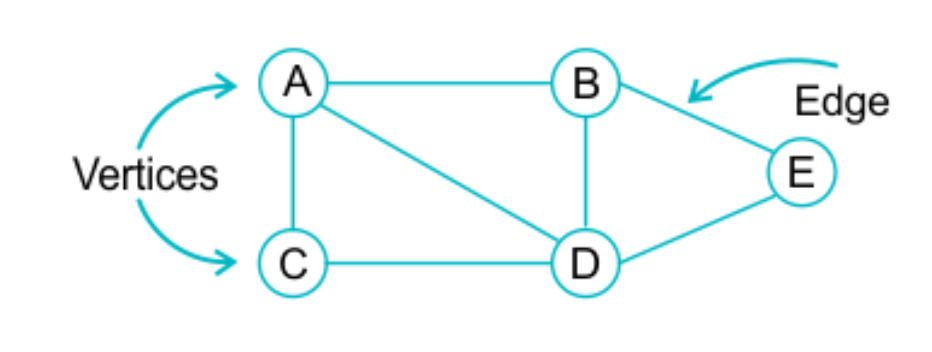
The direction of the edges determines the influence of one random variable on another. If the graph does not contain cycles (a number of vertices connected in a closed chain), it is usually referred to as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). Inference on these graphs may be performed exactly using algorithms such as Belief Propagation (BP) or variable elimination.