Cost Effectiveness Analysis
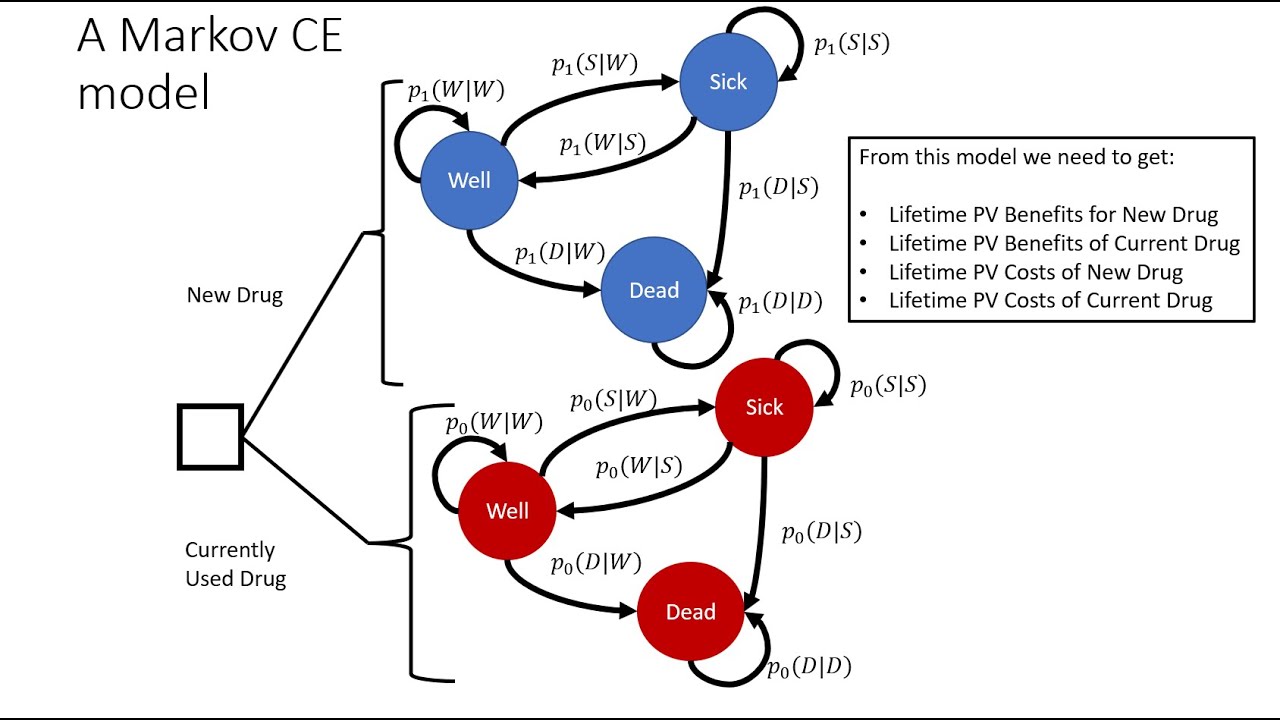
Markov models are widely used in cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) to evaluate the costs and benefits of different healthcare interventions over time. CEA is a method that compares the costs and outcomes of alternative interventions or treatments to determine which option provides the best value for money. In the context of CEA, Markov models are particularly useful for representing the natural progression of diseases or health states over time. They allow for the evaluation of long-term costs and outcomes by dividing the progression of a disease into a series of discrete health states, with patients transitioning between these states over time based on defined probabilities.